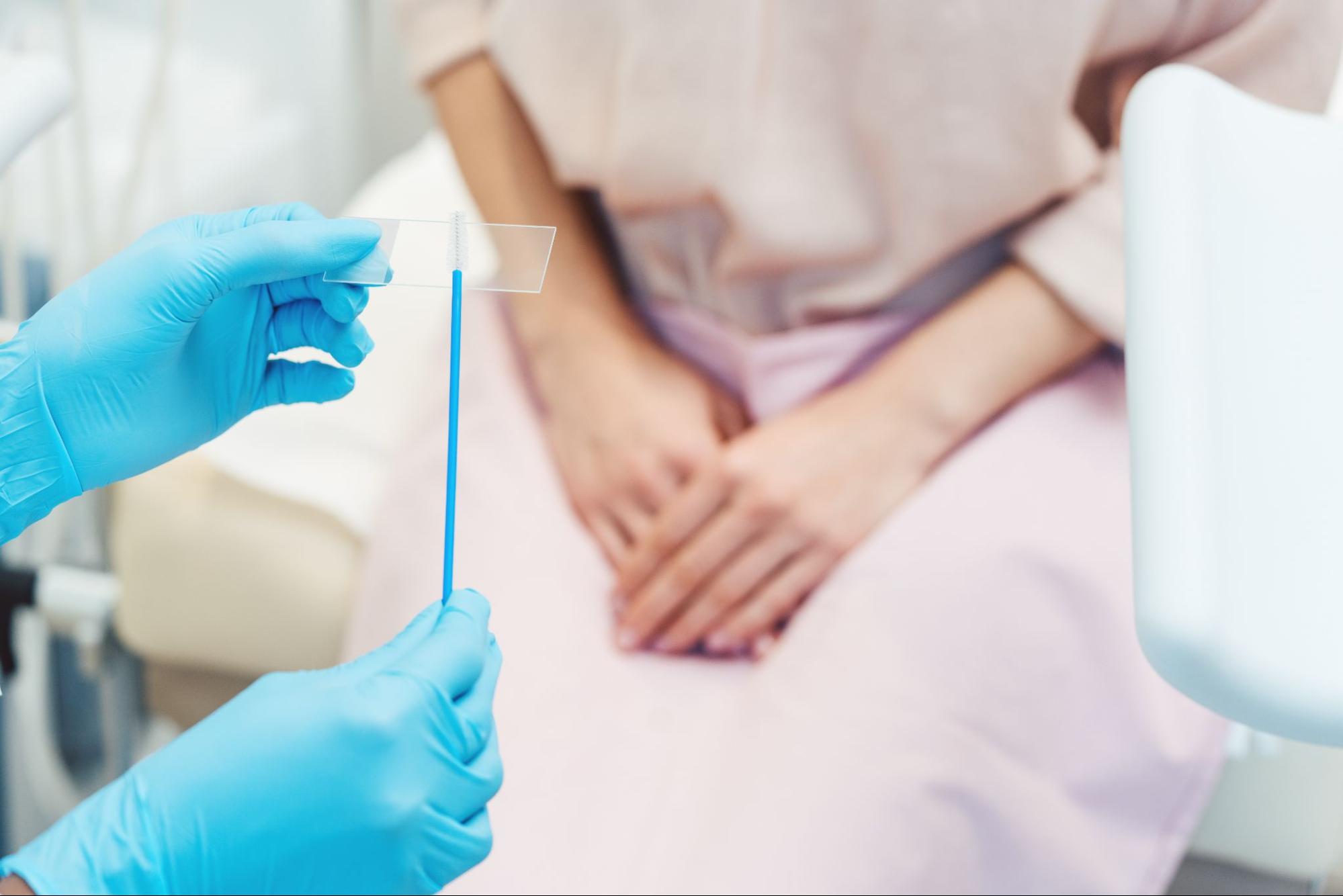
For many women, the idea of a Pap smear can be accompanied by a mix of emotions, ranging from anxiety to curiosity. However, understanding the procedure can go a long way in alleviating concerns and promoting confidence. A Pap smear is essential to women’s health and is designed to detect abnormal cervical cells that could indicate precancerous or cancerous changes. If you’re due for a Pap smear or simply want to know more, this guide will walk you through what to expect before, during, and after the procedure.
What is a Pap Smear?
A Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, is a screening procedure that checks for abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. This test is primarily used to detect cervical cancer and to identify precancerous cells caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Pap tests are typically recommended for women starting at age 21 and continuing through age 65, with frequency varying depending on your age, medical history, and the results of previous tests.
Before the Appointment: How to Prepare
Preparing for a Pap smear is simple, but there are a few steps you can take to ensure accurate results and a smoother experience:
- Schedule the Test for the Right Time:
- Aim to schedule your Pap smear when you are not menstruating, as blood can interfere with the test’s accuracy.
- Avoid Vaginal Products:
- Refrain from using tampons, douching, or applying creams or medications to your vagina for at least 48 hours before your appointment.
- Abstain from Intercourse:
- Avoid sexual activity for 24 to 48 hours before the test to ensure the most accurate results.
- Write Down Questions:
- If you have concerns or questions, jot them down beforehand to discuss with your provider.
- Choose Comfortable Clothing:
- Wear clothing that is easy to remove from the waist down to make the process more convenient.
What Happens During a Pap Smear?
Understanding each step of the Pap test can help demystify the process and ease any discomfort or anxiety:
Step 1: Checking In
When you arrive at your provider’s office, you’ll check in and may be asked to provide information about your menstrual cycle and medical history.
Step 2: Getting Ready
You’ll be directed to a private area to undress from the waist down. A gown or drape will be provided for your comfort.
Step 3: Positioning
You’ll lie down on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups, which allow the provider to access your cervix. While this position may feel awkward, try to relax—taking slow, deep breaths can help.
Step 4: Speculum Insertion
The provider will gently insert a speculum into your vagina. This device helps to hold the vaginal walls open, giving a clear view of your cervix. You may feel pressure, but it should not be painful. Let your provider know if you experience discomfort.
Step 5: Cell Collection
The provider collects a sample of cervical cells using a small brush or spatula. This quick process typically causes only mild sensations, such as light scraping or pressure.
Step 6: Removing the Speculum
The provider will carefully remove the speculum, and the procedure is complete. You can then get dressed.
After the Procedure: What to Expect
Most women can resume normal activities immediately after a Pap test. However, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Mild Spotting:
- It’s normal to experience light spotting for a day or two, especially if your cervix is sensitive. If spotting persists or becomes heavy, contact your provider.
- Results Timeline:
- Results are typically available within one to three weeks. Your provider’s office will inform you if further follow-up is needed.
- Next Steps for Abnormal Pap Test Results:
- If abnormal cells are detected, don’t panic. Many abnormalities are minor and resolve on their own. Your provider may recommend additional testing, such as an HPV test or a colposcopy, for further evaluation. Identifying abnormal cells early is a critical step in preventing cervical cancer.
Addressing Common Concerns
Will It Hurt?
Most women report that a Pap test is not painful, though it can be slightly uncomfortable. Communicating with your provider about any discomfort can help them adjust their approach.
Can I Still Get Tested If I’m Pregnant?
Yes, Pap tests are safe during pregnancy. Your provider may adjust the test timing based on your prenatal care plan.
What If I’m Nervous?
Feeling nervous is completely normal. Bring a trusted friend or family member for support, and don’t hesitate to share your concerns with your provider. Remember, the goal of the Pap test is to protect your health by detecting cervical cancer or precancerous changes early.
Why Are Pap Smears Important?
Routine Pap smears are crucial for detecting abnormal cells early, often before they progress to cervical cancer. They also play a vital role in monitoring reproductive health and identifying HPV-related changes.
You’re actively preventing cervical cancer by incorporating regular Pap smears into your healthcare routine. Early detection of abnormal cells can save lives and ensure the best possible health outcomes.
Key Benefits:
- Early detection of cervical cancer.
- Identification of HPV-related changes.
- Monitoring of reproductive health.
The connection between Pap tests and cervical cancer prevention cannot be overstated. By identifying abnormal cells before progressing to cancer, Pap tests have saved countless lives. Women who skip regular screenings are at a significantly higher risk of developing cervical cancer, which is often asymptomatic in its early stages.
When Should You Have a Pap Smear?
General Guidelines:
- Ages 21-29: Pap smear every 3 years.
- Ages 30-65: Pap tests combined with HPV testing every 5 years, or Pap smear alone every 3 years.
- 65 and Older: Testing may be discontinued if previous results have been normal.
Your provider may recommend a different schedule based on your medical history and risk factors. If you’ve had cervical cancer or precancerous changes in the past, you may need more frequent screenings.
Cervical Cancer and HPV: What You Need to Know
Cervical cancer is most commonly caused by persistent infection with certain strains of HPV. While HPV infections are very common and often clear on their own, some types of the virus can cause significant changes in cervical cells. Regular Pap and HPV tests are critical to catching these changes before progressing.
Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer:
- Persistent HPV infection.
- Smoking.
- A weakened immune system.
- Long-term use of birth control pills.
- Multiple full-term pregnancies.
- Early onset of sexual activity.
Prevention Tips:
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
- Attend regular Pap tests and follow your provider’s recommendations.
- Practice safe sex to reduce HPV transmission.
Tips for a Comfortable Experience
- Communicate: Let your provider know if you’re feeling anxious or experiencing discomfort.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, listening to calming music, or focusing on a positive thought can help.
- Stay Informed: Understanding what to expect can help reduce anxiety.
Conclusion
A Pap smear is a simple, quick procedure that plays a vital role in maintaining your health. You can confidently approach your appointment by understanding what to expect and how to prepare. Regular Pap smears are one of the most effective tools in the fight against cervical cancer, enabling early detection and intervention. Remember, your healthcare provider is there to ensure your comfort and to answer any questions you may have. If it’s time for your Pap smear, don’t delay—schedule an appointment today and take a proactive step toward your well-being.